Wait! Before You Go…
Let Aviox Technologies give your idea the edge it deserves — with a free:
- 🚀 Smart Project Blueprint
- 💰 Accurate Cost & Resource Estimate
- 📅 Launch Timeline Strategy


In this tutorial, you will dockerize a django application using Docker. Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker provides the ability to package and run an application in a isolated environment called a container. Containers are lightweight and contain everything needed to run your application, so you do not need to rely on what is currently installed on the host(Your Machine).
You need following things to start work:
$ python -m venv venv/
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ pip install django psycopg2-binary
Django is the framework that you will be using to develop your web app using python and psycopg2-binary is the python module which works as a adapter between postgresql and django.
$ django-admin startproject myproject
Now your project directory should look like this:
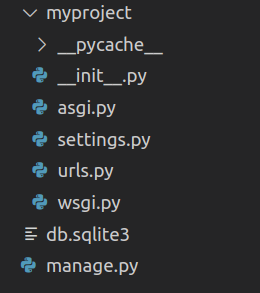
$ cd myproject
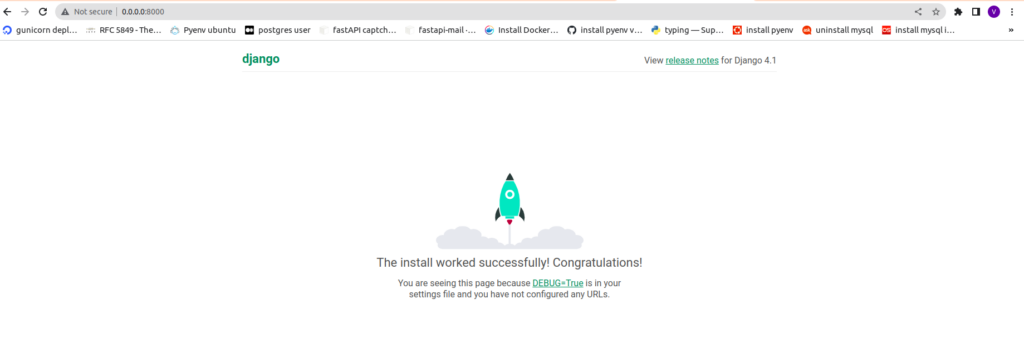
$ python manage.py runserver
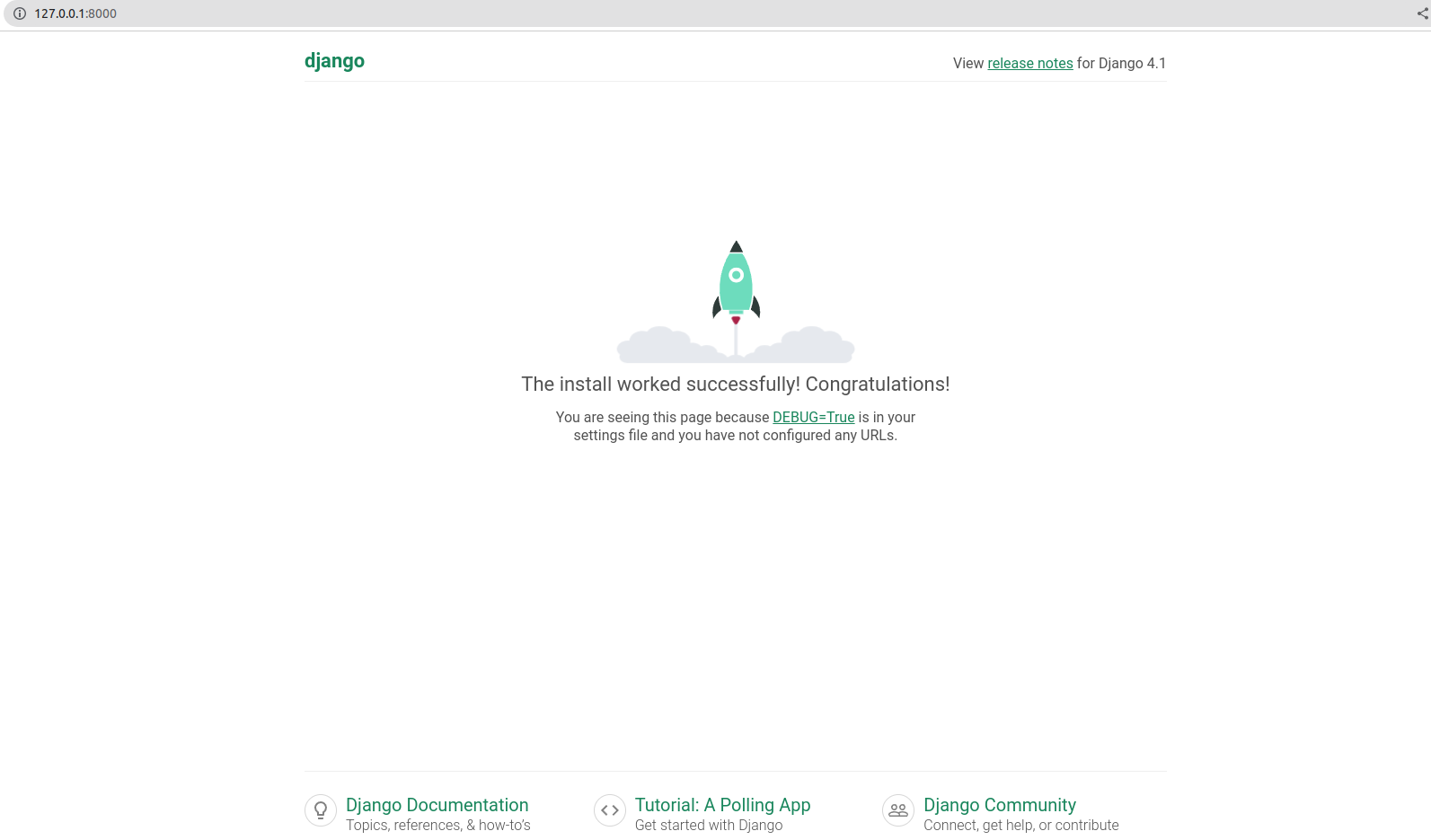
Kill the server once done by pressing ctrl+z.
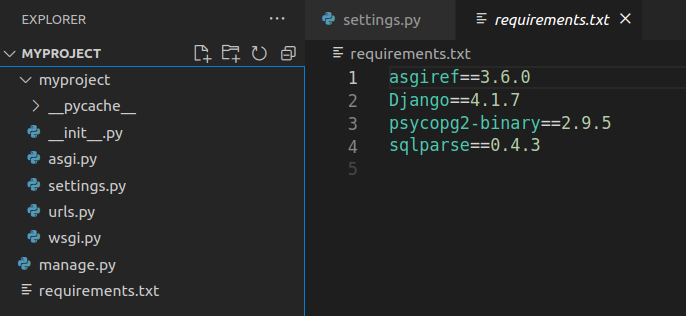
$ pip freeze > requirements.txt
Your project dependencies should have been included in requirements.txt file as shown in image:
deactivate

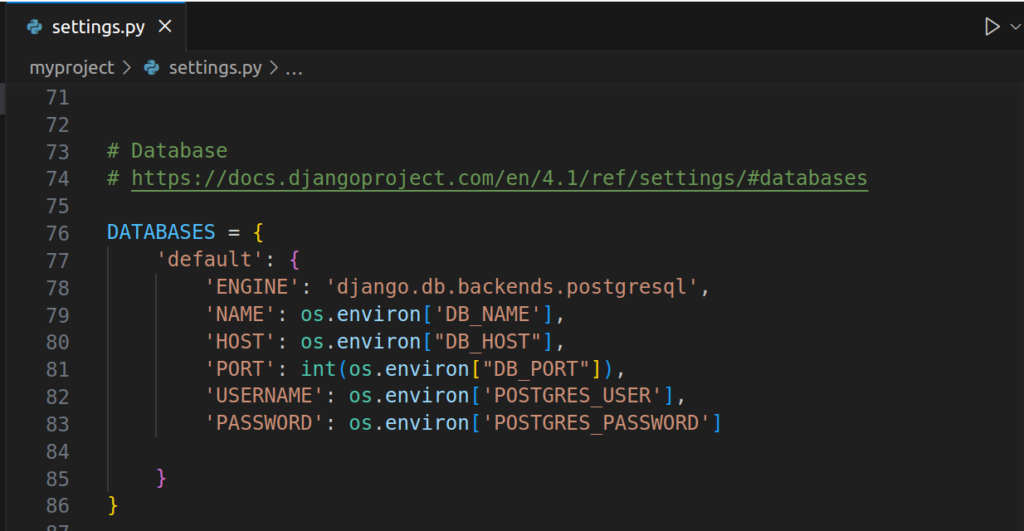
For now, You can set ALLOWED_HOST to ‘*’ to let the wsgi allow accepting http request from any domain but in production, this is not recommended.
services:
db:
image: postgres
ports:
- "5432:5432"
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=root
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
- POSTGRES_DB=root
healthcheck:
test: pg_isready
interval: 5s
timeout: 10s
retries: 120
web:
build: .
command: python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
volumes:
- .:/code
ports:
- "8000:8000"
environment:
- DB_NAME=root
- DB_PORT=5432
- DB_HOST=db
- POSTGRES_USER=root
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
depends_on:
- db
migration:
build: .
command: python manage.py migrate --noinput
volumes:
- .:/code
environment:
- DB_NAME=root
- DB_HOST=db
- DB_PORT=5432
- POSTGRES_USER=root
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=postgres
depends_on:
- db
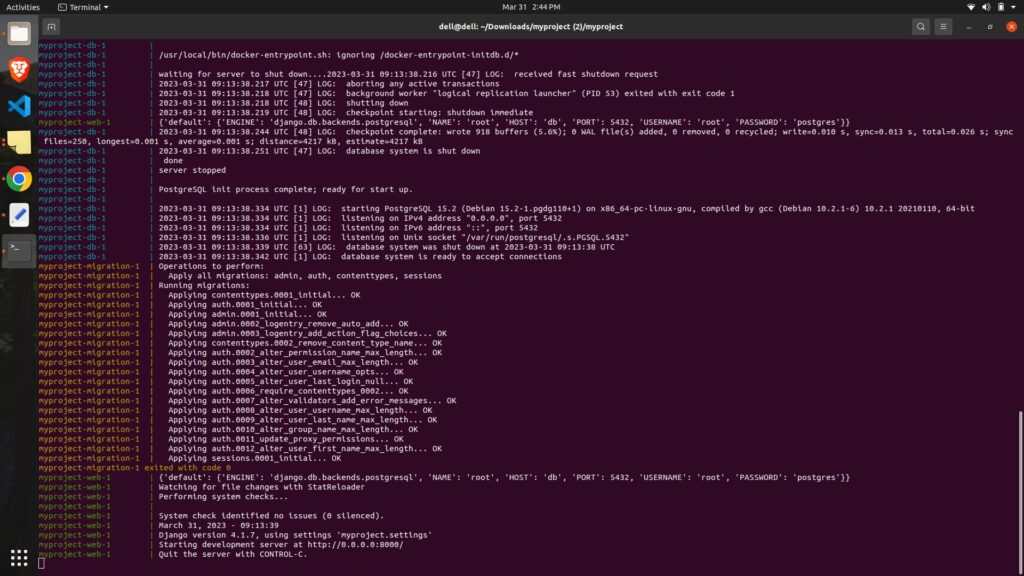
It should look like below:
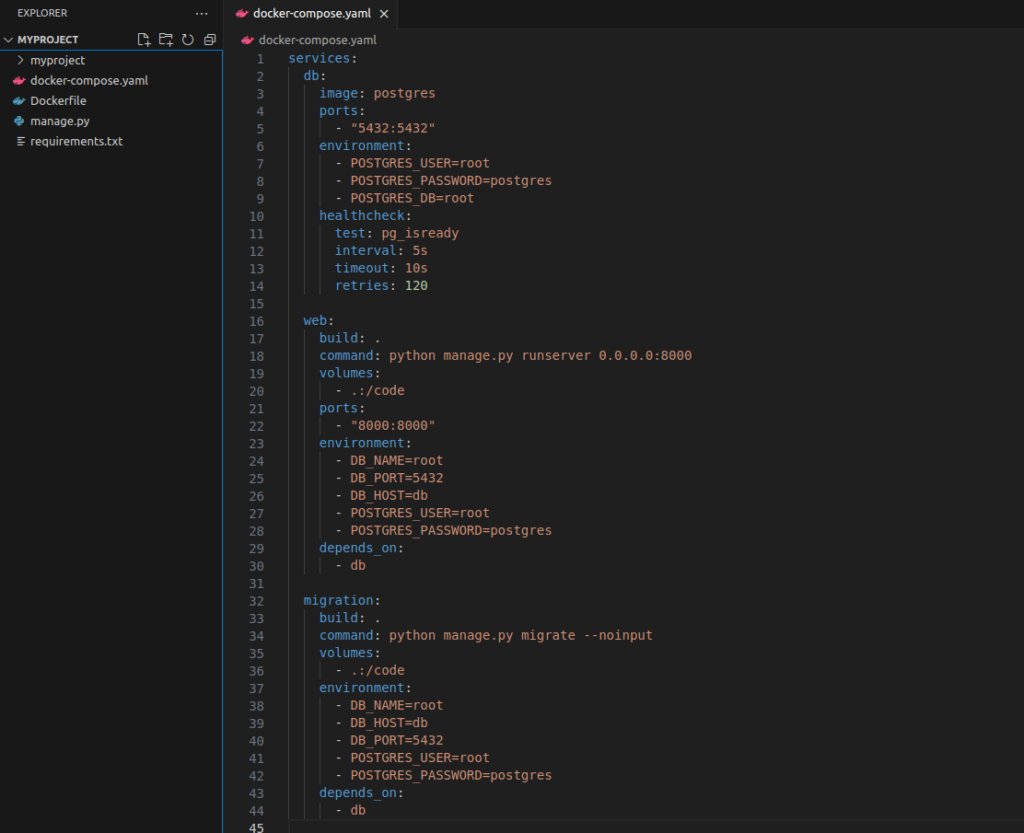
In docker-compose.yaml file, you define your services to be served inside your docker containers with specific syntax which docker will use to read and manage execution of defined services.
docker compose up --build

Get In touch
Our Testimonials: