Wait! Before You Go…
Let Aviox Technologies give your idea the edge it deserves — with a free:
- 🚀 Smart Project Blueprint
- 💰 Accurate Cost & Resource Estimate
- 📅 Launch Timeline Strategy

Vuex is a state management library for Vue.js, a popular front-end JavaScript framework. It provides a centralized store for managing the state of an application and facilitates communication between components.
### It is a self-contained app with the following parts:
If you’ve never built a large-scale SPA and jump right into Vuex, it may feel verbose and daunting. That’s perfectly normal – if your app is simple, you will most likely be fine without Vuex. A simple store pattern may be all you need. But if you are building a medium-to-large-scale SPA, chances are you have run into situations that make you think about how to better handle state outside of your Vue components, and Vuex will be the natural next step for you. There’s a good quote from Dan Abramov, the author of Redux:
If you are using Vuex, then you will have only one Single store for each VueJS powered application. Vuex Store is Singleton source of State. Our store contains application state. State management in VueJS with Vuex is straightforward. You just need to modify the state via dispatching the action and not directly because we want to predict the future states. Our store contains application state.
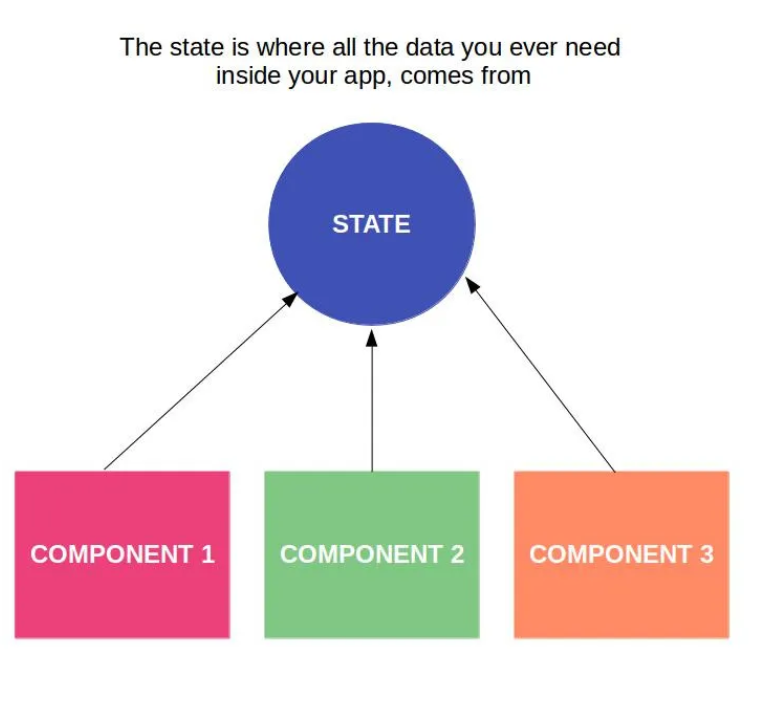
There is the only way to change the state in a Vuex store is by committing a mutation. We can change the state directly, but we will not do it because we need a snapshot for every project step. We need to predict the next state. For debugging, we will not mutate the state directly, but via mutations.
Actions are similar to mutations, the differences being that:
To add Vuex you can either do it through CDN links or preferably add it by running the following in your terminal in your project directory.
npm install vuex
or
npm add vuex
Next step will be to create our Vuex store:-
So in the src directory, create one folder called the store.
In that, create a file called store.js
//store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:{
},
getters:{
},
mutations:{
},
actions:{
},
modules:{
}
})
Here, I have imported Vuex store. We just pass this store, while creating vue instance in the main.js file.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
//TodoList.vue
<template>
<div>
Todos List
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//App.vue
<template>
<div>
<TodoList/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TodoList from './components/TodoList.vue'
export default{
components:{
TodoList
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//Todo.vue
<template>
<div>
Todo
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//TodoList.vue
<template>
<div>
<Todo/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Todo from './components/Todo.vue'
export default{
components:{
Todo
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//TodoForm.vue
<template>
<div>
TodoForm
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:{
todos:[
{
title: "todo item a",
completed: false
},
{
title: "todo item b",
completed: false
}
]
},
getters:{
},
mutations:{
},
actions:{
},
modules:{
}
})
//TodoList.vue
<template>
<div>
<Todo v-for="(todo,index) in todos" :key="index" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Todo from './components/Todo.vue'
export default{
components:{
Todo
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//Todo.vue
<template>
<div>
{{todo.title}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
props:['todo']
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//TodoForm.vue
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="newTodoItem"/>
<button>Submit</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
newTodoItem:""
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//TodoForm.vue
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="newTodoItem"/>
<button @click="addNewTodoItem()">Submit</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
data(){
return{
newTodoItem:""
},
},
methods:{
addNewTodoItem(){
this.$store.dispatch('addNewTodo',this.newTodoItem);
this.addNewTodoItem=""
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:{
todos:[
{
title: "todo item a",
completed: false
},
{
title: "todo item b",
completed: false
}
]
},
getters:{
},
mutations:{
NEW_TODO(state,todoItem){
state.todos.push({
title:todoItem,
completed: false
});
}
},
actions:{
addNewTodo({commit},todoItem){
commit('NEW_TODO',todoItem);
}
},
modules:{
}
})
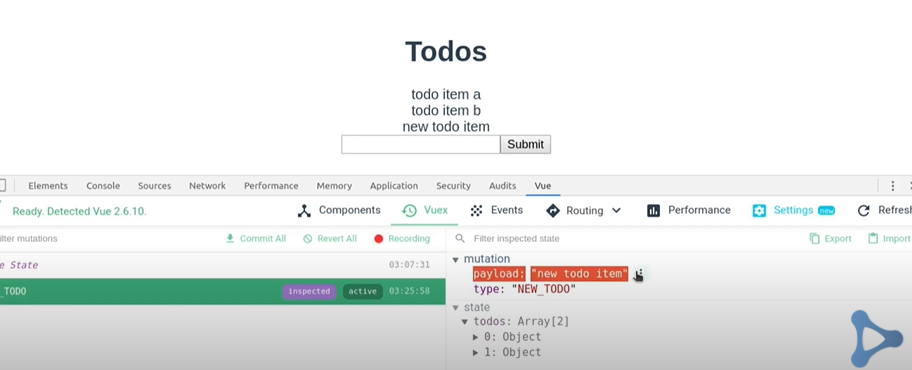
//Todo.vue
<template>
<div>
{{todo.title}}
<button @click="deleteTodo()">Delete</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
props:['todo']
},
methods:{
deleteTodo(){
this.$store.dispatch('deleteTodo',this.todo)
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
//store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state:{
todos:[
{
title: "todo item a",
completed: false
},
{
title: "todo item b",
completed: false
}
]
},
getters:{
},
mutations:{
NEW_TODO(state,todoItem){
state.todos.push({
title:todoItem,
completed: false
});
},
DELETE_TODO(state,todoItem){
let index= state.todos.indexOf(todoItem)
state.todos.splice(index,1);
}
},
actions:{
addNewTodo({commit},todoItem){
commit('NEW_TODO',todoItem);
},
deleteTodo({commit},todoItem){
commit('DELETE_TODO',todoItem);
}
},
modules:{
}
})
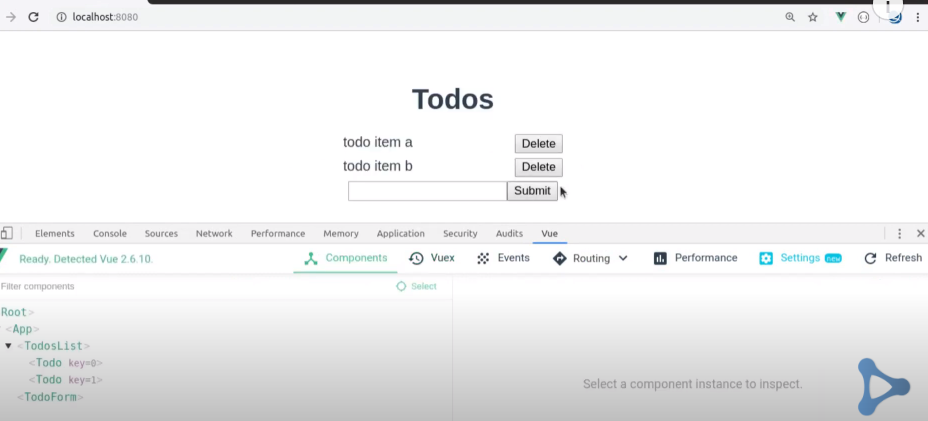

This is the basic of Vuex with an example of TODO APP

Get In touch
Our Testimonials: